Materiality of Kuraray Group
Materiality Specific Procedure
Procedure to Identify Materiality
Material issues (materiality) that the Kuraray Group should deal with on a priority basis have been identified in accordance with the following procedure. Materiality will be reviewed periodically in accordance with developments in the international community, changes in the business environment, and so on.
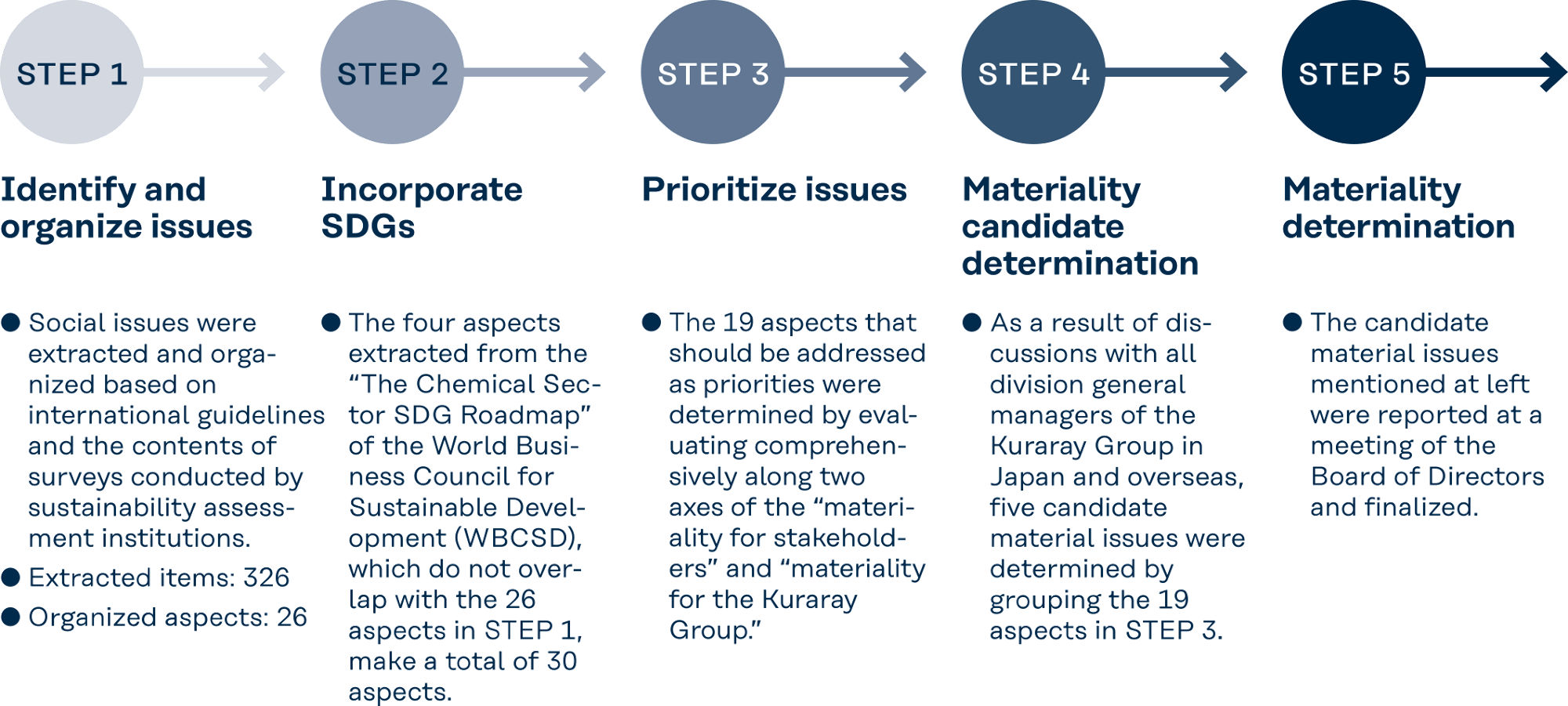
Step 1
The details of international guidelines and studies by sustainability assessment institutions that are used in extracting and summarizing social issues are as follows.
GRI, Environmental Reporting Guidelines (2012 Version), RBA, MSCI, FTSE4Good, DJSI, ISO26000, UN Global Compact, Green Paper EU, European Commission Strategy on CSR, German Stability Code, Circular Economy Package, American Chemistry Council
Step 2
The four aspects extracted from the “The Chemical Sector SDG Roadmap” of the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) are as follows:
Food disposal, water processing, climate change, and people’s health and wellness
Step 3
The materiality matrix of the Kuraray Group, which evaluates comprehensively by using the two axes of the “materiality for stakeholders” and “materiality for the Kuraray Group” is shown below.
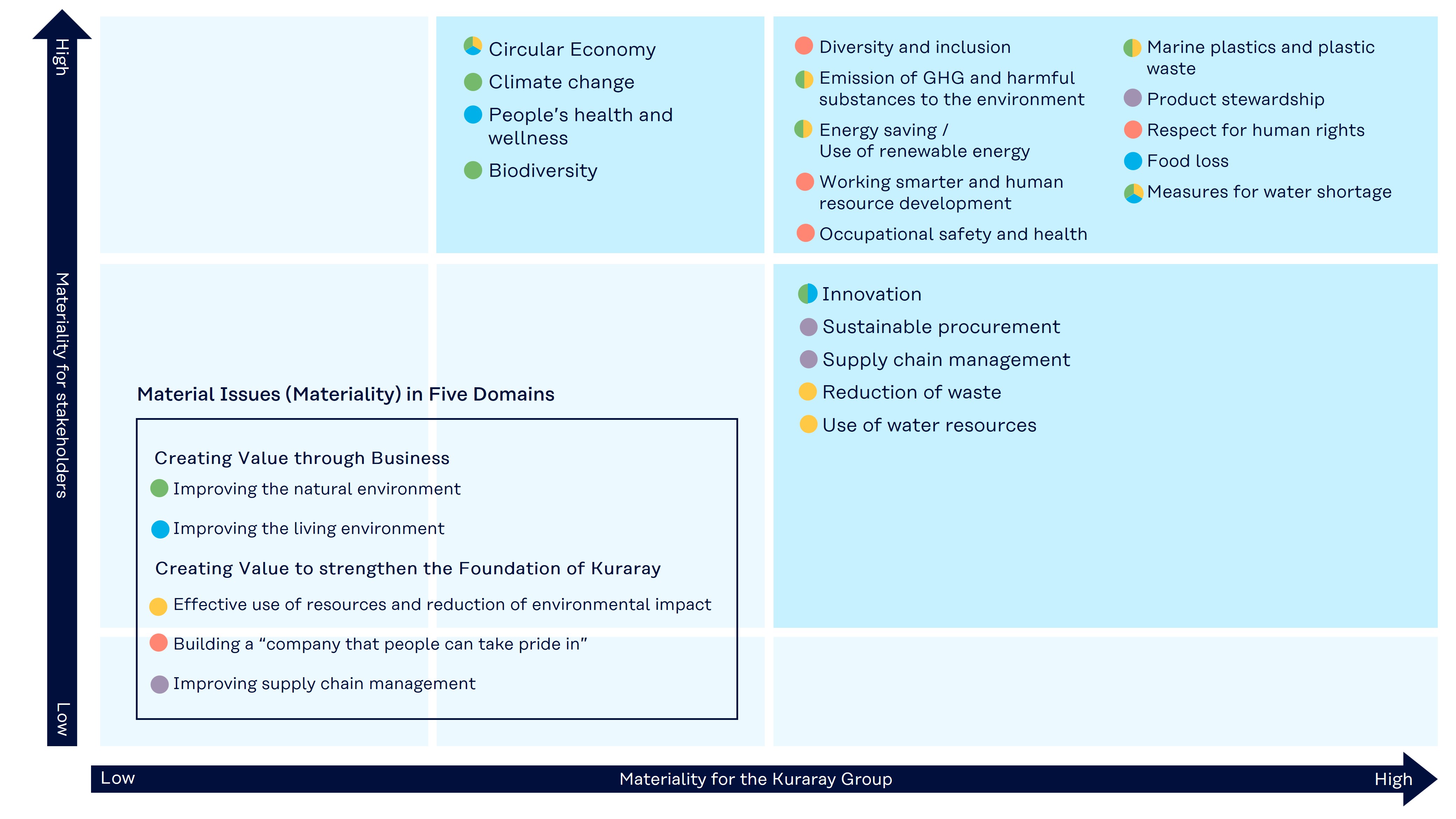
Materiality Matrix of the Kuraray Group
“Corporate governance,” “CSR management,” “ethics/code of conduct,” “risk management,” “relationships with stakeholders,” and “top statement” are to be dealt with separately from materiality.
As a result, materiality that the Kuraray Group is expected to deal with on a priority basis were identified as the following 19 aspects:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diversity and inclusion | Emission of GHG and harmful substances to the environment | Energy saving / Use of renewable energy | Working smarter and human resource development | Occupational safety and health |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marine plastics and plastic waste | Product stewardship | Respect for human rights | Food loss | Measures to water shortage |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Economy | Climate change | People’s health and wellness | Biodiversity | Innovation |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Procurement | Supply chain management | Reduction of wastes | Use of water resources |
Step 4
The 19 aspects identified in Step 3 were grouped to determine the following five items of “improving the natural environment,” “improving the living environment,” “effective use of resources and reduction of environmental impact,” “improving supply chain management,” and “building a ‘company that people can take pride in’” as materiality candidates.
In addition, “improving the natural environment” and “improving the living environment” were grouped under the broad category of “creating value through business,” with “effective use of resources and reduction of environmental impact,” “improving supply chain management,” and “building a ‘company that people can take pride in’” under “creating value to strengthen the foundation of Kuraray.”
| Materiality | The 19 aspects identified in the materiality matrix | |
|---|---|---|
| Creating Value through Business | Improving the Natural Environment | 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15 |
| Improving the Living Environment | 9, 10, 11, 13, 15 | |
| Creating Value to Strengthen the foundation of Kuraray | Effective Use of Resources and Reduction of Environmental Impact | 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 18, 19 |
| Improving supply chain management | 7, 16, 17 | |
| Building a "company culture we can be proud of" | 1, 4, 5, 8 |
Step 5
The materiality candidates determined in Step 4 were reported to and approved by the Board of Directors.
